Guiyang
A city with humid subtropical climate, Guiyang is surrounded by mountains and forest. The area, inhabited since at least the Spring and Autumn period, formally became the capital of the surrounding province in 1413, during the Yuan dynasty. The city is home to a large Miao and Bouyei ethnic minority population. Guiyang has a diversified economy, traditionally a center for aluminum production, phosphate mining, and optical instrument manufacturing. Following reforms, the majority of the city's economic output in the services sector. Since 2015, it has seen targeted investments into big data and quickly emerged as a local innovation hub.
Guiyang is one of the top 500 science cities in the world by scientific research outputs, as tracked by the Nature Index. The city is also home to Guizhou University, a national research university under the Project 211 and under the Double First Class Status in certain disciplines.
The valley approximating present-day Guiyang has been inhabited since the Spring and Autumn period. Guiyang was a 7th-century military outpost under the Sui and Tang, when the area around it was known as Juzhou. It grew into a city named Shunyuan under the Mongolian Yuan dynasty sometime between their 1279 southwestern campaigns and 1283. By the time Guizhou became a full province in 1413, its capital at Guiyang was also known as Guizhou. It became a prefectural seat under the Ming and Qing. Guiyang grew rapidly during the development of the southwest that occurred after the Japanese invasion of China during World War II. It has also grown rapidly since Deng Xiaoping's economic reforms reached it in the 1990s.
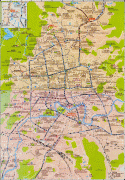
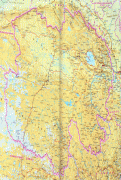
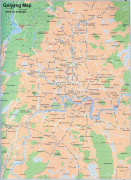
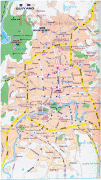
Map - Guiyang
Map
Country - China
 |
 |
| Flag of China | |
Modern Chinese trace their origins to a cradle of civilization in the fertile basin of the Yellow River in the North China Plain. The semi-legendary Xia dynasty in the 21st century BCE and the well-attested Shang and Zhou dynasties developed a bureaucratic political system to serve hereditary monarchies, or dynasties. Chinese writing, Chinese classic literature, and the Hundred Schools of Thought emerged during this period and influenced China and its neighbors for centuries to come. In the third century BCE, Qin's wars of unification created the first Chinese empire, the short-lived Qin dynasty. The Qin was followed by the more stable Han dynasty (206 BCE–220 CE), which established a model for nearly two millennia in which the Chinese empire was one of the world's foremost economic powers. The empire expanded, fractured, and reunified; was conquered and reestablished; absorbed foreign religions and ideas; and made world-leading scientific advances, such as the Four Great Inventions: gunpowder, paper, the compass, and printing. After centuries of disunity following the fall of the Han, the Sui (581–618) and Tang (618–907) dynasties reunified the empire. The multi-ethnic Tang welcomed foreign trade and culture that came over the Silk Road and adapted Buddhism to Chinese needs. The early modern Song dynasty (960–1279) became increasingly urban and commercial. The civilian scholar-officials or literati used the examination system and the doctrines of Neo-Confucianism to replace the military aristocrats of earlier dynasties. The Mongol invasion established the Yuan dynasty in 1279, but the Ming dynasty (1368–1644) re-established Han Chinese control. The Manchu-led Qing dynasty nearly doubled the empire's territory and established a multi-ethnic state that was the basis of the modern Chinese nation, but suffered heavy losses to foreign imperialism in the 19th century.
Currency / Language
| ISO | Currency | Symbol | Significant figures |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNY | Renminbi | ¥ or 元 | 2 |
| ISO | Language |
|---|---|
| ZH | Chinese language |
| UG | Uighur language |
| ZA | Zhuang language |